What is Manufacturing Process?
Manufacturing process is basically a complex activity, concerned with people who've a broad number of disciplines and expertise and a wide range of machinery, tools, and equipment with numerous levels of automation, such as computers, robots, and other equipment. Manufacturing pursuits must be receptive to several needs and developments.
In this blog I will be telling you about the forming methods of a newer material in manufacturing i.e. FRP (Fiber Reinforced Polymers).
Fiber-reinforced polymers (FRPs) are a type of composite plastics made of a matrix or binding agent reinforced by a fiber material. The FRP process thus entails two steps: making the fibrous material and bonding the material with a polymer plastic.

Fiber Manufacture:
Fiber preforms are manufactured through weaving, braiding, stitching, and knitting. Weaving is used in making both two-dimensional and three-dimensional fibers and is suitable for the manufacture of high-value and narrow-width products.
It has its downsides, though. For one, weaving multi-layer fibers is time-consuming and fairly more expensive. Also, it is difficult to create fabrics with fibers that are oriented to each other at anything other than 90-degree angles.
Braiding is way better in that aspect as it allows for fibers to be aligned at 45 degrees to each other. Through two-step braiding, manufacturers can create right about any shape of preform.
Knitting typically produces two-dimensional fabric, but the creation of multi-layer fabric is possible with machines fitted with more than one needle bed.
Stitching is perhaps the most straightforward technique of creating preforms and is revered for its suitability in both pre-preg and dry fabric stitching.
Forming Processes:
Bonding the fiber and the polymer plastic is the second and most critical part of FRP manufacture. It can be achieved through several processes, including:
- Hand Lay-up
- Spray Up method
- Filament winding
- Match Die Molding
- Pultrusion
- Resin transfer molding
- Reaction injection molding, etc.
1)Hand Layup Method:
- Hand Lay-Up is well suited for low volume production of product. This method can be used for both corrosion barrier and the structural portion. A mold must be used for hand lay-up parts unless the composite is to be joined directly to another structure. The mold can be as simple as a flat sheet or have infinite curves and edges. For some shapes, molds must be joined in sections so they can be taken apart for part removal after curing. Reinforcement fibers can be cut and laid in the mold. It is up to the designer to organize the type, amount and direction of the fibers being used. Resin must then be catalyzed and added to the fibers. A brush or roller can be used to impregnate the fibers with the resin. – The lay-up technician is responsible for controlling the amount of resin and the quality of saturation.
Copyright © 2018. EPP Composites Pvt Ltd
 |
| Copyright © 2018. EPP Composites Pvt Ltd |
- Resins: – Any, e.g. epoxy, polyester, vinyl ester, phenolic.
- Fibers: – Any, although heavy aramid fabrics can be hard to wet-out by hand.
- Advantages:
- Widely used for many years.
- Simple principles to teach.
- Low cost tooling, if room-temperature cure resins are used.
- Wide choice of suppliers and material types.
- Higher fiber contents, and longer fibers than with spray lay-up.
- Disadvantages
- Resin mixing, laminate resin contents, and laminate quality are very dependent on the skills of laminators.
- Low resin content laminates cannot usually be achieved without the incorporation of excessive quantities of voids.
- Health and safety considerations of resins.:
- The lower molecular weights of hand lay-up resins generally means that they have the potential to be more harmful than higher molecular weight products. The lower viscosity of the resins also means that they have an increased tendency to penetrate clothing etc.
- Resins need to be low in viscosity to be workable by hand. This generally compromises their mechanical/thermal properties due to the need for high diluents levels.
- Generally large in size but low in production quantity - not economical for high production.
- Applications:
- Boat hulls
- Swimming pools
- Large container tanks
- Movie and stage props
- Other formed sheets
- • The largest molding ever made was ship hulls for the British Royal Navy: 85 m (280 ft) long
- 2)Spray up method:

- © 2019 NetComposites
 |
|
- Fiber is chopped in a hand-held gun and fed into a spray of catalyzed resin directed at the mold. The deposited materials are left to cure under standard atmospheric conditions.
- • Materials Options:
- Resins: Primarily polyester. Fibers: Glass roving only.
- Advantages:
- Continuous process
- Any materials can be used as mold.
- Error can be corrected by re-spraying
- Disadvantages:
- Slow.
- inconsistency.
- No control of fiber orientation.
- Only one side finished.
- Environmental unfriendly.
- 3) Pultrusion:
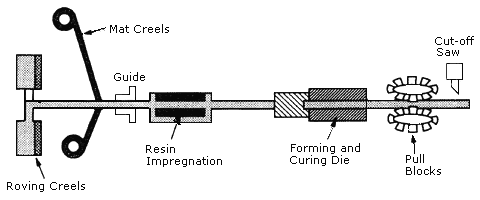
- Fibers are pulled from a creel through a resin bath and then on through a heated die. The die completes the impregnation of the fiber, controls the resin content and cures the material into its final shape as it passes through the die. This cured profile is then automatically cut to length. Fabrics may also be introduced into the die to provide fiber direction other than at 0°. Pultrusion is a continuous process, producing a profile of constant cross-section, a variant known as 'pulforming' allows for some variation to be introduced into the cross- section.
- Advantages:
- This can be a very fast, and therefore economic, way of impregnating and curing materials.
- Resin content can be accurately controlled.
- Fiber cost is minimized since the majority is taken from a creel.
- Structural properties of laminates can be very good since the profiles have very straight fibers and high fiber volume fractions can be obtained.
- Resin impregnation area can be enclosed thus limiting volatile emissions.
- Disadvantages:
- Limited to constant or near constant cross-section components
- Heated die costs can be high.
- Typical Applications:
- Beams and girders used in roof structures, bridges, ladders, frameworks.
- 4) Filament Winding:


- This process is primarily used for hollow, generally circular or oval sectioned components, such as pipes and tanks.
- Fiber tows are passed through a resin bath before being wound onto a mandrel in a variety of orientations, controlled by the fiber feeding mechanism, and rate of rotation of the mandrel
- Advantages
- This can be a very fast and therefore economic method of laying material down.
- Resin content can be controlled by metering the resin onto each fiber tow through nips or dies.
- Fiber cost is minimized since there is no secondary process to convert fiber into fabric prior to use.
- Structural properties of laminates can be very good since straight fibers can be laid in a complex pattern to match the applied loads.
- Disadvantages
- The process is limited to convex shaped components.
- Fiber cannot easily be laid exactly along the length of a component.
- Mandrel costs for large components can be high.
- The external surface of the component is unmolded, and therefore cosmetically unattractive.
- Low viscosity resins usually need to be used with their attendant lower mechanical and health and safety properties.
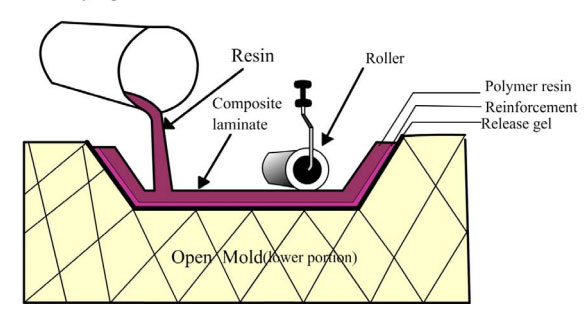
- 5) Resin transfer molding:

© 2008-2020 ResearchGate GmbH
 |
| © 2008-2020 ResearchGate GmbH |
- Resin transfer molding is a closed molding process In this technique, as the name indicates, resin is transferred over the already placed reinforcement. Reinforcement in terms of either woven mat or strand mat form is placed on the surface of lower half mold. A release gel is applied on the mold surface for easy removal of the composite. The mold is properly closed and clamped. The clamping can be done either perimeter clamping or press clamping mechanism The resin is pumped into the mold through ports and air is displaced through other vents After curing, the mold is opened and composite product is taken out.
- Raw materials :
- Matrix- Epoxy, Methyl Methacrylate, polyester, polyvinyl ester, phenolic resin.
- Reinforcement- Glass fiber, carbon fiber, aramid fiber, natural plant fibers(sisal, banana,nettle, hemp, flax, etc).
- These fibers are used either individually or in combined form as a woven mat , unidirectional mat or chopped strand mat.
- Mineral fillers may also be added to improve surface finish and fire retardant.
- Advantages
- Composite part produced with this method has good surface finish on both side surface of the product.
- Any combination of reinforced materials (including 3D) in any orientation can be achieved.
- Fast cycle time can be achieved through temperature control tooling device.
- Process can be manual control, semi-automated or highly automated.
- Composite part thickness is uniform which is determined by the mold cavity.
- The process does not require high injection pressure
- Disadvantages
- Mold cavity limits the size of the composite.
- High tooling cost.
- There is limitation on reinforcing materials due to the flow and resin saturation of fibers.
- 6) Reaction injection molding :

©1999-2020. The Open University
 |
©1999-2020. The Open University
|
- Reaction injection molding (RIM) is similar to injection molding except thermosetting polymers are used, which requires a curing reaction to occur within the mold. First, the two parts of the polymer are mixed together. The mixture is then injected into the mold under high pressure using an impinging mixer. The mixture is allowed to sit in the mole long enough for it to expand and cure. If reinforcing agents are added to the mixture then the process is known as reinforced reaction injection molding (RRIM). Common reinforcing agents include glass fibers and mica. This process is usually used to produce rigid foam automotive panels
- Advantages and disadvantages:
- • Reaction injection molding can produce strong, flexible, lightweight parts which can easily be painted
- • It also has the advantage of quick cycle times compared to typical vacuum cast materials.
- • The bi-component mixture injected into the mold has a much lower viscosity than molten thermoplastic polymers, therefore large, light-weight, and thin-walled items can be successfully RIM processed.
- • This thinner mixture also requires less clamping forces, which leads to smaller equipment and ultimately lower capital expenditures.
- • Another advantage of RIM processed foam is that a high- density skin is formed with a low-density core.
- • The disadvantages are slow cycle times, compared to injection molding, and expensive raw materials.
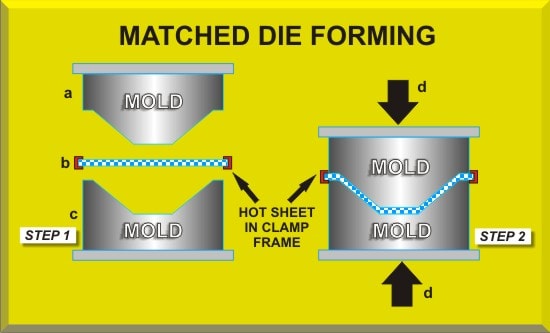
- 7) Matched die forming :
Copyright © 2004-2019 K & K Tool & Die Co.,Ltd.
 |
| Copyright © 2004-2019 K & K Tool & Die Co.,Ltd. |
- a) Matched-die molding:
- The composite material is pressed between heated matched dies
- Pressure required depends on the flow characteristics of the feed materials
- The feed materials flows into the contours of the mold and cures at high temp.
- The types of matched die forming are:
- Sheet molding compound (SMC)
- Dough/bulk molding compound (DMC)
- These three molding technique utilize same type of high pressure molding equipment but differ in the form of the material that is placed inside the mold to form the part
- a) Sheet molding compound (SMC)
- Sheet of resin-fiber blend which contains additives (curing agent, release agent & pigments). Clean to be used & give good consistency in properties
- SMC molding is a sheet material that is made by chopped glass fibers on to a sheet of plastic film on which a resin- initiator-filler mixture has been doctored. Another film which also has the resin mixture applied onto it, is placed on the top and then the sandwich of resin mixture and the chopped glass is passed between the compaction rolls to wet the fibers and mix the constituents. The material is then cured and rolled up for shipment. A typical SMC incorporates about 30- 50% fibers ,25%resin,25-45%filler.
- b) Dough molding compound (DMC/BMC)
- Blends (in dough forms) of all the necessary constituents (but only short fibers are used).
- BMC is a dough like mixture of chopped fiberglass resin initiator and fillers that has a composition similar to that of SMC. The resulting material is called a premix. The fiberglass mixture is about 5-10% lower than SMC . BMC is molded by placing a weighed amount of material onto the lower mold .The mold are then closed under pressure ,temperature.
- Advantages
- • Both interior and exterior surfaces are finished
- • Production rate can be high
- • Labour cost are low
- • Minimum trimming of parts are molded
- • Product has good mechanical properties and closed part tolerance
- Disadvantages
- • More equipment is needed than layup
- • Mould and tooling are costly than layup molds
- • Transparent parts are not possible with SMC and BMC
- • Molding problems may cause surface imperfections
- • SMC and BMC have limited shelf life

Well explained!
ReplyDeleteHelpful
ReplyDeleteUnique topic! Very well explained. Covered almost all the details.
ReplyDeleteVery informative
ReplyDeleteToooo goooooood👍
ReplyDeleteThis comment has been removed by a blog administrator.
ReplyDeleteVery informative!
ReplyDeleteNoice.very well explained
ReplyDeleteInspired!
ReplyDeleteGreat Work!!
ReplyDelete